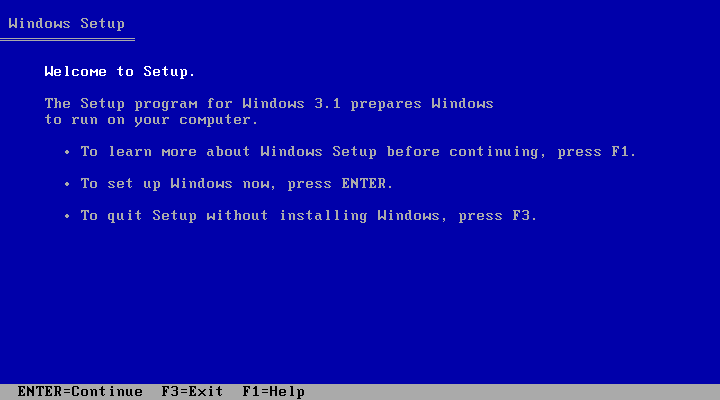
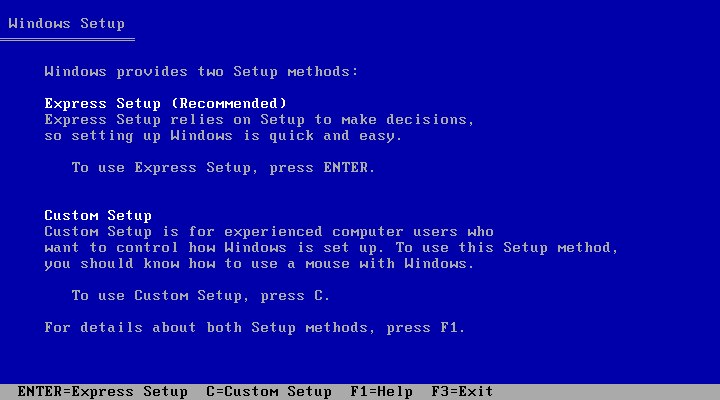
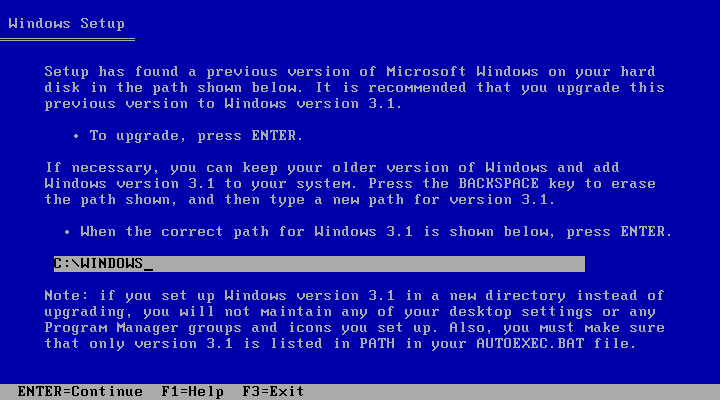
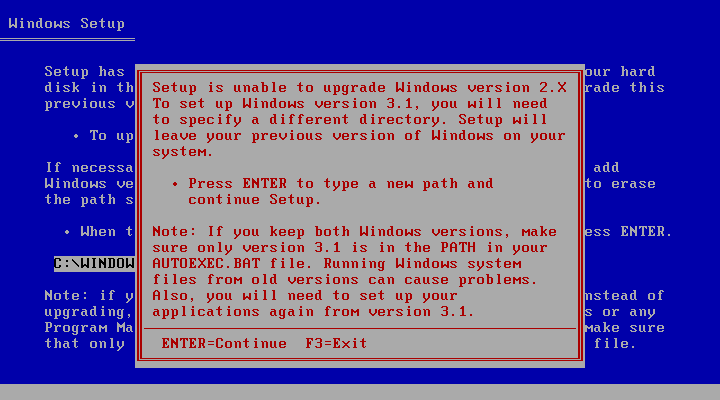
This one-liner (source):
I found this batch script/command on ServerFault *I think*. Very cool little one-liner trick.
@for %%e in (%PATHEXT%) do @for %%i in (%1%%e) do @if NOT "%%~$PATH:i"=="" echo %%~$PATH:i
Example usage:
C:\Users\Rich\Desktop>whereis cmd C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe C:\Users\Rich\Desktop>whereis shutdown C:\Windows\System32\shutdown.exe C:\Users\Rich\Desktop>whereis putty
Update: July 21, 2011 So, I discovered: “where” built-in to Windows…
Description: Displays the location of files that match the search pattern. By default, the search is done along the current directory and in the paths specified by the PATH environment variable.
“where” exists in Windows Server 2003 but I also have it natively on Windows Vista and 7. Not sure which other Windows releases it is included in.